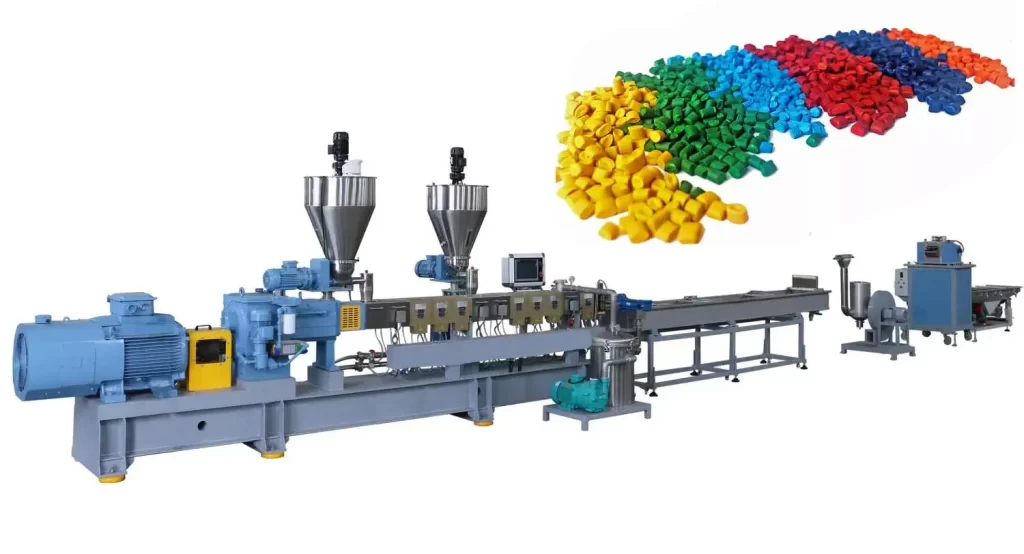
Extruder
An extruder is a machine that melts and forces a rubber or plastic mixture to pass through a die at the end of the machine, producing a continuous product with a specific cross-section. Extruder machines are widely used in the rubber and plastics industry for a variety of applications. In the production line, extruder machines are used for the initial shaping of rubber and plastic for subsequent processing, as well as for shaping final products. All of these applications require the practical needs of each specific application to be designed into the machine, and the wide range of available extruder machine designs reflects this.
Products produced with extruder:
- Types of hoses
- Tire Crunch (Tire Crunch)
- Tire sidewall (side part of the tire tread)
- Masterbatch
- White masterbatch
- Color masterbatch
- Black masterbatch
- Additive masterbatch
- Polymer compound
- Sealants
- Profiles and strips
- Wires and cables, and in general, all products that are continuous.
Classification of extruders in terms of feeding:
Extruders are divided into two categories based on the temperature of the materials fed to them, which is necessary for the operation:
- Hot feed extruder
- Cold feed extruder
The feed required for hot extruders used in the rubber industry is usually preheated in a separate operation. In conventional hot extrusion methods, a single die is usually used for this purpose. Cold extruders operate using a rubber strip or rubber pellets at ambient temperature. Secondly, extruders can be classified and separated according to their application. Many factories want a machine that, if not efficient enough, can at least successfully and correctly process a variety of compounds with different mixtures. The emphasis here is on minimizing die change times and returning the machine to proper operating condition and the ease of cleaning necessary and sufficient to minimize contamination from compound changes. When a machine is to operate for a long time with rubber compounds that have limited fluidity and flow properties, the screw conveyors can be designed to provide both high material output and good dimensional control. Also, despite minor changes in the feed material, the feed section and tension belt, as well as the control system, can be selected to achieve good dimensional control.
Major physical differences between cold and hot extruders
The main physical difference between cold and hot extruders is the ratio of the length to the diameter of their screw. For hot machines, where a significant portion of the energy is spent heating and plasticizing the rubber mixture on the shaft, the extruder screw simply transfers and applies pressure.
This makes the machines small and has screw lengths of 3d to 5d in relation to their diameter. In addition to the transfer and pressure operations of the screw, in cold extruders the screw must be able to perform the necessary mechanical work on the rubber to raise the temperature and reach the desired temperature and create softness of the material when it exits the die. This allows the screws to have longer lengths in the range of 9d to 15d, and in some applications even larger screws may be used.
Cold extruders have largely replaced hot types in production lines. This replacement has mostly been done in lines that required long-term work or accuracy in measuring correct dimensions. This machine, with its significant advances resulting from the diversity of designs developed and knowledge of working techniques, has made a significant contribution to capturing the machinery market.
Overview of cold-feed screw extruder components:
Feeding hopper: This is the place where the mixture (materials) enters the extruder. The shape of the hopper varies depending on the type of feeding.
Two things are important about the feeding funnel:
- Funnel size
- Feeding uniformity
Uniform feeding produces a uniform product.
Extruder shell or body:
It is a metal cylinder that surrounds the screw. Holes are made inside this cylinder so that we can control the temperature of the extruder by passing hot and cold water. If the temperature of the mixture is not controlled, the mixture will heat up, which will cause the output product to come out roasted or burnt (or basically scorched).
Spiral:
In a cold-feed extruder, as the name suggests, the rubber compound is fed at ambient temperature. The feed may be in the form of strips or pellets. The screw must transfer sufficient mechanical energy to both soften the compound and counteract the back pressure of the die.
Special considerations are required in the design of the screws used in a cold-feed extruder. In order to achieve the required amount of mastication, the height of the screw blade must be low and the length of the screw long.
The screw of a simple extruder has three feeding sections, a transfer or metering section, and a compression section. Each section of the screw has a separate role. The feeding section transfers the material from the feed hopper. The transfer section heats and mixes the material.
The compression section is the homogenizer and creates the pressure necessary to push the material through the die.
There is also temperature control within the screw. The spiral has channels through which water can pass to control the temperature. The speed of the spiral has a great effect on the temperature of the extruder. At a constant feed rate, increasing the speed of the spiral increases the temperature of the product exiting the extruder.
Ideal speed in screw extruders:
It is the speed limit that can receive the rubber from the feed and prevent it from accumulating in the feed hopper.
Head:
The purpose of using the head is to balance and uniform the pressure and transfer the mixture to the mold.
The shape of the head must be designed to meet the following needs:
- Ensuring maximum output without any problems or irregularities
- Compensation of deformation due to elastic recovery properties of the mixture
- Elimination of stagnant and static areas that may be created along the mixing path.
Mold (Die):
A die is a body that is placed on the head and causes the mixture to take the desired shape when it comes out. In general, die design requires a lot of skill and experience.
To understand what an extruder is and how it works? First, we need to know what the extrusion process is?
The main function of the extrusion process is to easily convert brittle materials into the desired product. It can be claimed that extrusion is a semi-continuous or even continuous process that is used to form hot or even cold materials.
Plastic extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which a polymeric material, enriched with the desired additives, is melted and formed in a continuous process. The raw material (polymer) is a granule that enters a hopper by gravity and falls onto a rotating screw through a feed throat. The screw rotation is performed by an electric motor. The screw design varies and depends on the material and the design of the final product.
The rotation of the screw pushes the plastic through a heated barrel. As the plastic moves through the barrel, the channel or thread of the screw narrows, compressing the plastic. Three or more PID controllers heat the barrel. The temperature of the molten plastic is usually higher than the temperature set for the controllers. This additional heat is generated through a combination of compressive force and shear friction (shear heat).
When the molten plastic reaches the end of the screw, it is forced through a plate. The device filters out contaminants. Finally, the filtered melt is pushed through a die. The die gives the final product the desired specifications and shape. After exiting the extruder, the final product is cooled. The method of cooling depends on the specifications and shape of the extrudate.
Now, let’s continue the article to discuss the difference between extrusion and extruder and basically, what is an extruder?
What is an extruder?
An extruder is a machine used in the extrusion process. The same process of producing plastic materials as mentioned above is carried out by an extruder. Extruders are divided into two categories: single-screw extruders and twin-screw extruders.
What is the difference between extruder and extrusion?
Extrusion is a shaping method used to reduce the thickness or cross-section of materials. In fact, extrusion is a process by which materials are produced in a desired shape. The best way to compare extrusion and extruder is to say: “Extrusion is a production line for various plastic materials.” In contrast, an extruder is a set of chambers and screws that are responsible for producing plastic materials as a machine.
An extruder is a machine that melts plastic dough and passes it through a die under pressure to create a product with a specific cross-section. In fact, an extruder is a machine in an extrusion production line. Extrusion is a method or process, but extrusion is also known as a plastic production machine or device.
Extrusion is a process, but an extruder is a machine. Plastic materials are placed in an extruder machine to perform the extrusion process. This process means converting molten plastic materials into finished products by applying pressure. So extrusion can be called a production line in which the extruder is a part of the equipment. When purchasing, you should mention the term extrusion production line so that the seller understands your needs well.
Extruder components
Extruders consist of three main parts: the feed zone, the compression zone, and the metering zone. Due to the wide range of applications of this device, they are used in various sectors of the rubber and plastic industries. The most common extruders are divided into two categories: single-screw and twin-screw.
Single screw extruder
A method of shaping plastics is extrusion, which consists of a screw. This model is capable of extruding materials without tolerances, so that it is both efficient in terms of material and energy consumption. Other features of this machine are long life, high production capacity and desirable quality of products.
The main parts of a single-screw extruder are divided into 5 main parts, which are also shown in the figure:
- Drive system
- Feeding system
- Cylinder (screw, shell and heating system)
- Die and head assembly
- Control system
The components of the extruder are made up of various parts, such as the hopper, screw, barrel, and die, which we will mention separately below. The electrical part of the device also consists of a controller, thermocouple, and electric heaters.
Funnel
Due to the nature of gravity, hoppers are the first place where polymer particles enter the extruder as raw materials. Different types of hoppers are available in small and large sizes, depending on the volume of input materials. The hoppers used in extruders are similar in shape to those used in general applications. Most hoppers used in extruders can be installed on the system via bolts and nuts. These hoppers can also be replaced and moved.
Heater
The heater’s job is to heat the chamber inside the cylinder, which heats the system by being placed around the cylinder. Ultimately, the materials inside the cylinder melt due to the heat and become ready to be shaped and formed.
Die
At the beginning of the barrel or extruder chamber, there is a frangible plate that is connected to the die. The dies are actually the molds in which the material is formed. It can be said that the final shaping of the product is done by them. In this way, the molten material is poured into the mold dies and is transformed into the desired shape by the shaping process. The interchangeable feature of the dies allows the system to produce a variety of shapes.
Screw and cylinder
The screw refers to a metal, screw-like piece that is one of the main components in the extruder. The function of the screws is to convert raw materials into dough-like materials. In fact, using a screw or screw, the materials entering the hopper can be pushed towards the chamber. Given the sensitivity and importance of this part of the device, it is better to use the utmost care in its design and production. In case of improper design, it may cause instability in the products produced. The speed of the screws used in the extruder is adjustable.
The screw is kept in a chamber called a cylinder. In addition to holding the screw, the cylinder is also responsible for heat transfer and temperature stabilization. The cylinders do this by using cold and hot water holes.
Description of the single screw extruder
The raw materials are fed into the screw in the form of granules or soft soil from the hopper and then heated by the heat generated by the barrel heaters and the shear caused by the movement on the edges of the screw. As the depth of the passage decreases, the length of the screw decreases, resulting in the compression of the materials.
At the end of the machine, where the work is output, the molten materials are transformed into the desired shape for the final product by passing through various molds. Single screws are mainly used to produce various types of polyethylene pipes.
Description of the Domardone extruder
Another type of extruder is the twin-screw extruder, which uses two screws in opposite directions and some in the same direction. This type of extruder usually has three times the production capacity of single-screw extruders.
In a twin-screw extruder with opposite directions of rotation, the material undergoes shearing and compression (as occurs in a roller mill), meaning the material is compressed between rollers with different directions of rotation. In an extruder with two screws with the same direction of rotation, the material is transferred from one screw to the other.
This type of arrangement is perfectly suitable for heat-sensitive materials, because the material is transferred quickly in the extruder without the slightest possibility of entrapment. The movement of the material around the uncoupled screws is slower, but the propulsive force is greater.
Application of extruders
Products processed from extruders can be divided into the following groups:
- Rods and Profiles
- Tubes
- Films and Sheets
- Monofilaments
- Extrusion Coatings
- Wire and Cable Coatings
Shaping methods using an extruder:
Extrusion is a very flexible method that, using the appropriate extrusion process, can produce a wide range of products.
- Granular production
- Profile production
- Ultra-thin sheet production by blow molding
- Blow molding
Final words
The extrusion process is one of the most common processes in today’s manufacturing world, and the extruder is one of the advanced tools in the field of thermoplastic materials production. In addition to producing plastic parts from raw materials, this machine is also capable of recycling plastic waste. The extruder is used to manufacture a variety of profile, sheet and pipe products.
Kimia Trava Tek Company, a manufacturer Masterbatch ,Types of compounds, Black masterbatch و Additive masterbatch It is of the best quality.